装饰者模式(Decorator),动态地给一个对象添加一些额外的功能,就增加功能来说,装饰者模式比继承更灵活。
装饰者模式解析

角色介绍
Component:定义一个对象接口,可以给这些对象动态地添加功能。
ConcreteComponent:是定义了一个具体的对象,也可以给这个对象添加一些功能。
Decorator:装饰抽象类,继承了 Component,从外类来扩展 Component 类的功能,但对于 Component 来说,是无需知道 Decorator 的存在的.
ConcreteDecorator(A/B):具体的装饰对象,起到给 Component 添加功能的作用。
装饰者模式基本代码
- Component 类
1 | /** |
2 | * Component |
3 | */ |
4 | public interface Component { |
5 | |
6 | void operation(); |
7 | } |
- ConcreteComponent 类
1 | /** |
2 | * @author star |
3 | */ |
4 | public class ConcreteComponent implements Component { |
5 | |
6 | |
7 | public void operation() { |
8 | System.out.println("具体的操作"); |
9 | } |
10 | } |
- Decorator 类
1 | /** |
2 | * Decorator |
3 | */ |
4 | public abstract class Decorator implements Component { |
5 | |
6 | protected Component component; |
7 | |
8 | public Decorator(Component component) { |
9 | this.component = component; |
10 | } |
11 | |
12 | |
13 | public void operation() { |
14 | if (this.component == null) { |
15 | return; |
16 | } |
17 | // 执行功能 |
18 | this.component.operation(); |
19 | } |
20 | } |
- ConcreteDecoratorA 类
1 | /** |
2 | * ConcreteDecoratorA |
3 | */ |
4 | public class ConcreteDecoratorA extends Decorator { |
5 | |
6 | public ConcreteDecoratorA(Component component) { |
7 | super(component); |
8 | } |
9 | |
10 | |
11 | public void operation() { |
12 | // 执行原 Component 对象的功能 |
13 | super.operation(); |
14 | // 执行本类的功能 |
15 | System.out.println("装饰者 A 的操作"); |
16 | } |
17 | } |
- ConcreteDecoratorB 类
1 | /** |
2 | * ConcreteDecoratorB |
3 | */ |
4 | public class ConcreteDecoratorB extends Decorator { |
5 | |
6 | public ConcreteDecoratorB(Component component) { |
7 | super(component); |
8 | } |
9 | |
10 | |
11 | public void operation() { |
12 | // 执行原 Component 对象的功能 |
13 | super.operation(); |
14 | // 执行本类的功能 |
15 | System.out.println("装饰者 B 的操作"); |
16 | } |
17 | } |
- Main 类
1 | /** |
2 | * Main |
3 | */ |
4 | public class Main { |
5 | |
6 | public static void main(String[] args) { |
7 | // 装饰组件 |
8 | ConcreteDecoratorB decoratorB = new ConcreteDecoratorB(new ConcreteDecoratorA(new ConcreteComponent())); |
9 | |
10 | decoratorB.operation(); |
11 | } |
12 | } |
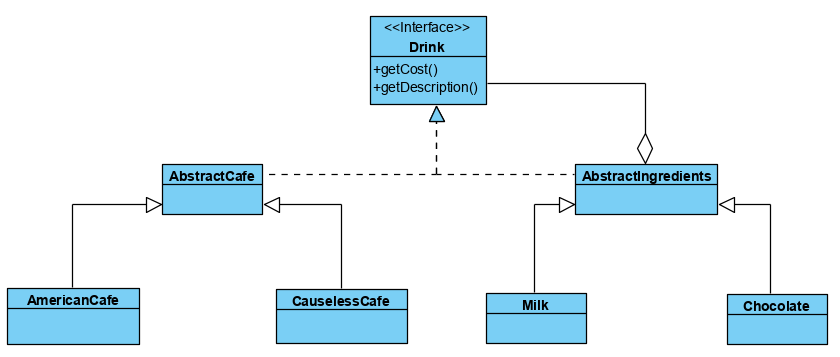
示例
咖啡订单程序,咖啡种类有美式咖啡(American coffee)、无因咖啡(Causeless coffee),配料有牛奶(Milk),巧克力(Chocolate)。客户在点咖啡时可以选择配料进行混合。使用装饰者模式编程代码。
类结构图
编码
- Drink 类
1 | /** |
2 | * Drink |
3 | */ |
4 | public abstract class Drink { |
5 | |
6 | protected String name; |
7 | |
8 | protected float price; |
9 | |
10 | public abstract float getCost(); |
11 | |
12 | public abstract String getDescription(); |
13 | |
14 | public String getName() { |
15 | return name; |
16 | } |
17 | |
18 | public void setName(String name) { |
19 | this.name = name; |
20 | } |
21 | |
22 | public float getPrice() { |
23 | return price; |
24 | } |
25 | |
26 | public void setPrice(float price) { |
27 | this.price = price; |
28 | } |
29 | } |
- Cafe 类
1 | /** |
2 | * Cafe |
3 | */ |
4 | public class Cafe extends Drink { |
5 | |
6 | |
7 | public float getCost() { |
8 | return this.price; |
9 | } |
10 | |
11 | |
12 | public String getDescription() { |
13 | return "商品:" + this.name + "价格:" + this.price; |
14 | } |
15 | |
16 | } |
- AmericanCafe 类
1 | /** |
2 | * AmericanCafe |
3 | */ |
4 | public class AmericanCafe extends Cafe { |
5 | |
6 | public AmericanCafe() { |
7 | this.name = "美式咖啡"; |
8 | this.price = 6.0f; |
9 | } |
10 | |
11 | } |
- CauselessCafe 类
1 | /** |
2 | * CauselessCafe |
3 | */ |
4 | public class CauselessCafe extends Cafe { |
5 | |
6 | public CauselessCafe() { |
7 | this.name = "无因咖啡"; |
8 | this.price = 7.0f; |
9 | } |
10 | } |
- AbstractIngredients 类
1 | /** |
2 | * AbstractIngredients |
3 | */ |
4 | public class AbstractIngredients extends Drink { |
5 | |
6 | private Drink drink; |
7 | |
8 | public AbstractIngredients(Drink drink) { |
9 | this.drink = drink; |
10 | } |
11 | |
12 | |
13 | public float getCost() { |
14 | return super.price + this.drink.getCost(); |
15 | } |
16 | |
17 | |
18 | public String getDescription() { |
19 | return drink.getDescription() + "配料:" + this.name + " 价格:" + this.price ; |
20 | } |
21 | } |
- Milk 类
1 | /** |
2 | * Milk |
3 | */ |
4 | public class Milk extends AbstractIngredients { |
5 | |
6 | public Milk(Drink drink) { |
7 | super(drink); |
8 | this.name = "牛奶"; |
9 | this.price = 3.0f; |
10 | } |
11 | } |
- Chocolate 类
1 | /** |
2 | * @author star |
3 | */ |
4 | public class Chocolate extends AbstractIngredients { |
5 | |
6 | public Chocolate(Drink drink) { |
7 | super(drink); |
8 | this.name = "巧克力"; |
9 | this.price = 2.0f; |
10 | } |
11 | } |
- Main 类
1 | /** |
2 | * Main |
3 | */ |
4 | public class Main { |
5 | |
6 | public static void main(String[] args) { |
7 | // 牛奶巧克力美式咖啡 |
8 | Drink drink = new Chocolate(new Milk(new AmericanCafe())); |
9 | |
10 | System.out.println(drink.getDescription()); |
11 | System.out.println(drink.getCost()); |
12 | |
13 | } |
14 | } |
小结
一般情况下,当系统需要新功能的时候,是向旧的类中添加新的代码。这些新加的代码通常装饰了原有类的核心职责或主要行为,但这种做法的问题在于,它们在主类中加入了新的字段,新的方法和新的逻辑,从而增加了主类的复杂度,而这些新加入的东西仅仅是为了满足一些只在某种特定情况下才执行的特殊行为的需要。
而装饰者模式却提供了一个非常好的解决方案,装饰者模式是为已有功能动态地添加更多功能的一种方式,它把每个要装饰的功能放在单独的类中,并让这个类包装它所要装饰的对象,因此,当需要执行特殊行为时,客户代码就可以在运行时根据需要有选择地、按顺序地使用装饰功能包装对象了。
装饰者模式的好处就是有效地把类的核心职责和装饰功能区分开了,而且可以去除相关类中重复的装饰逻辑。